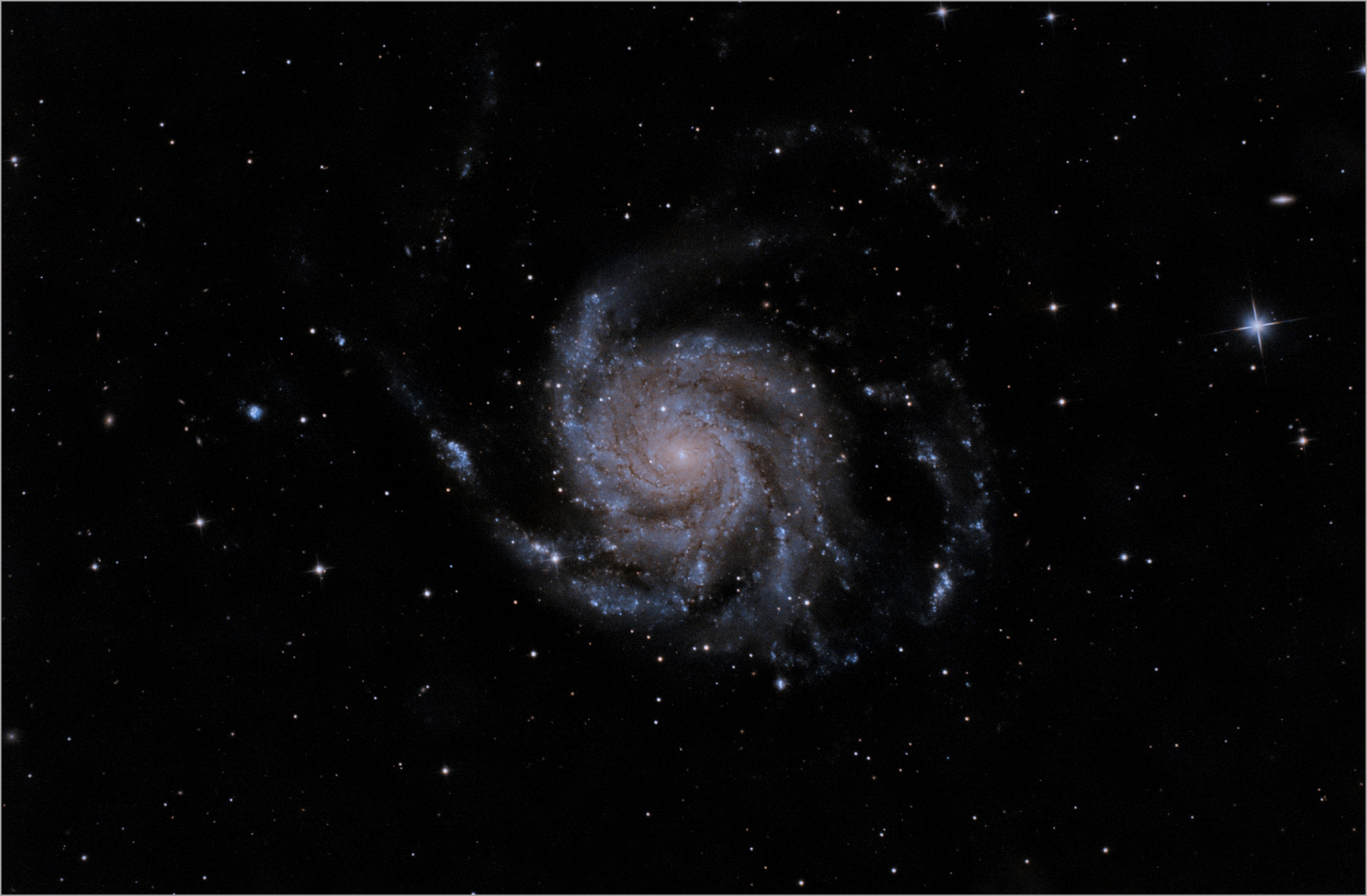

| M101 |
| The Pinwheel Galaxy in the Constellation Ursa Major and New Supernova SN 2023ixf Imaged June 21st, 2023 |
 |
One of the last entries in Charles Messier's famous catalog, big, beautiful spiral galaxy M101 is definitely not one of the least. About 170,000 light-years across, this galaxy is enormous, almost twice the size of our own Milky Way Galaxy. Also known as the Pinwheel Galaxy, M101 lies within the boundaries of the northern constellation Ursa Major, about 25 million light-years away. Recently, in May, 2023, a Type II supernova was discovered and is shown in the images displayed on this webpage. See below sections for more information about the supernova.
Image information courtesy of
NASA,
SEDS, and
Wikipedia.
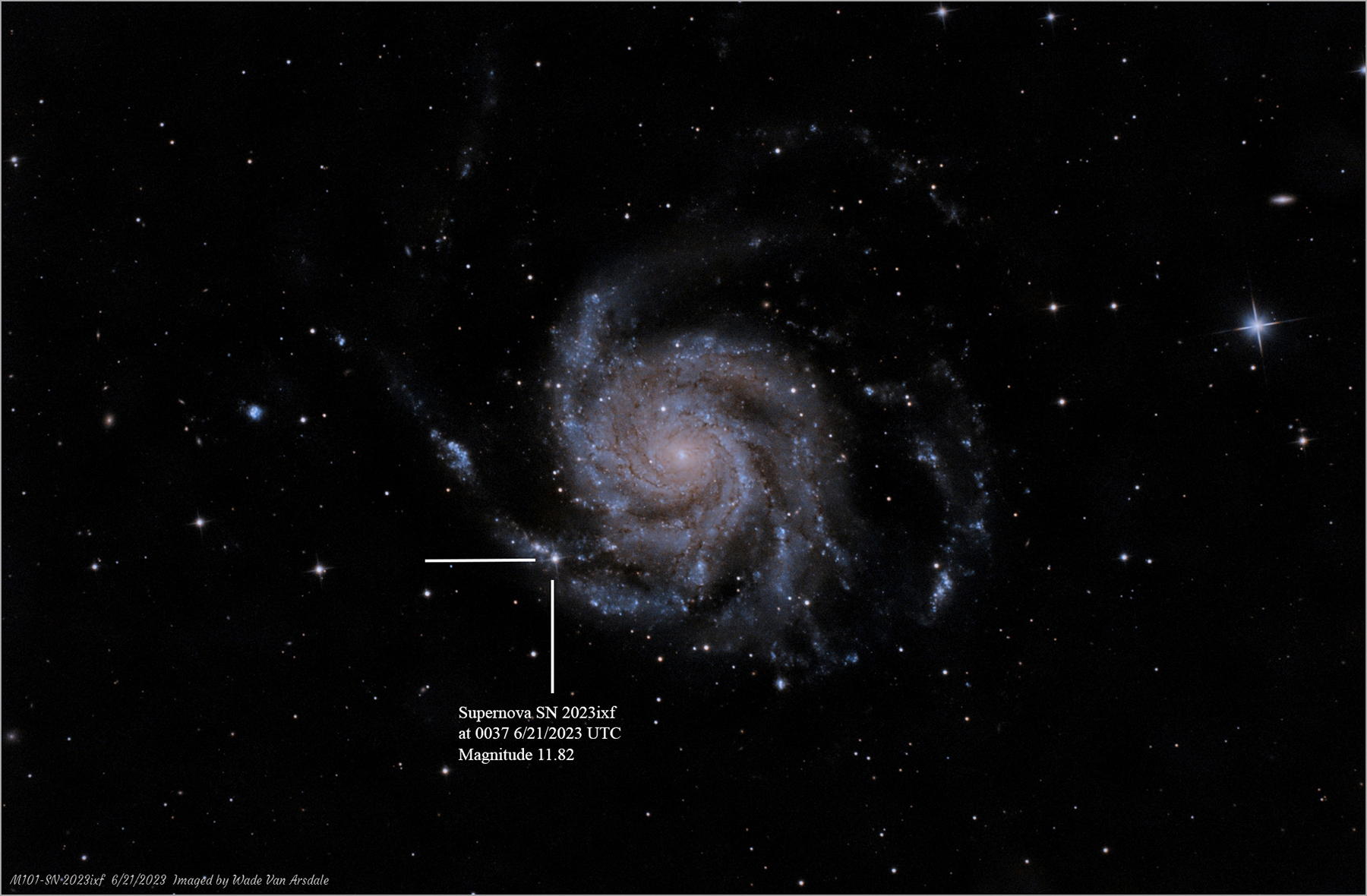
Image Details: See Supernova SN 2023ixf Information and Identifiers Below that Point Out the Supernova Location Within the Galaxy
Supernova SN 2023ixf
Information (courtesy of
WikiPedia):
The supernova was
first observed on 19 May 2023 by
astronomer Koichi
Itagaki and immediately classified as a type II supernova. Initial
magnitude at discovery was 14.9. After
discovery, the
Zwicky Transient Facility project found a
pre-discovery image of the supernova at
magnitude 15.87 two days before discovery. The supernova is about 21
million light-years from Earth and is expected
to have left behind either a
neutron star or
black hole based on current
stellar evolution models.
See Supernova SN
2023ixf Locator Image below:
For
more SN 2023ixf data and image links, go to the
Rochester Academy of Science Astronomy Section
website.
 |
Supernova SN2023ixf Photometry Data:
Brightness Measurements and Methodology:
●
Maxim
DL/CCD 5 software was used to derive the brightness level of the supernova
as it appeared on June 21st, 2023, slightly over one month post-discovery.
● The Photometry Tool inside Maxim was calibrated to
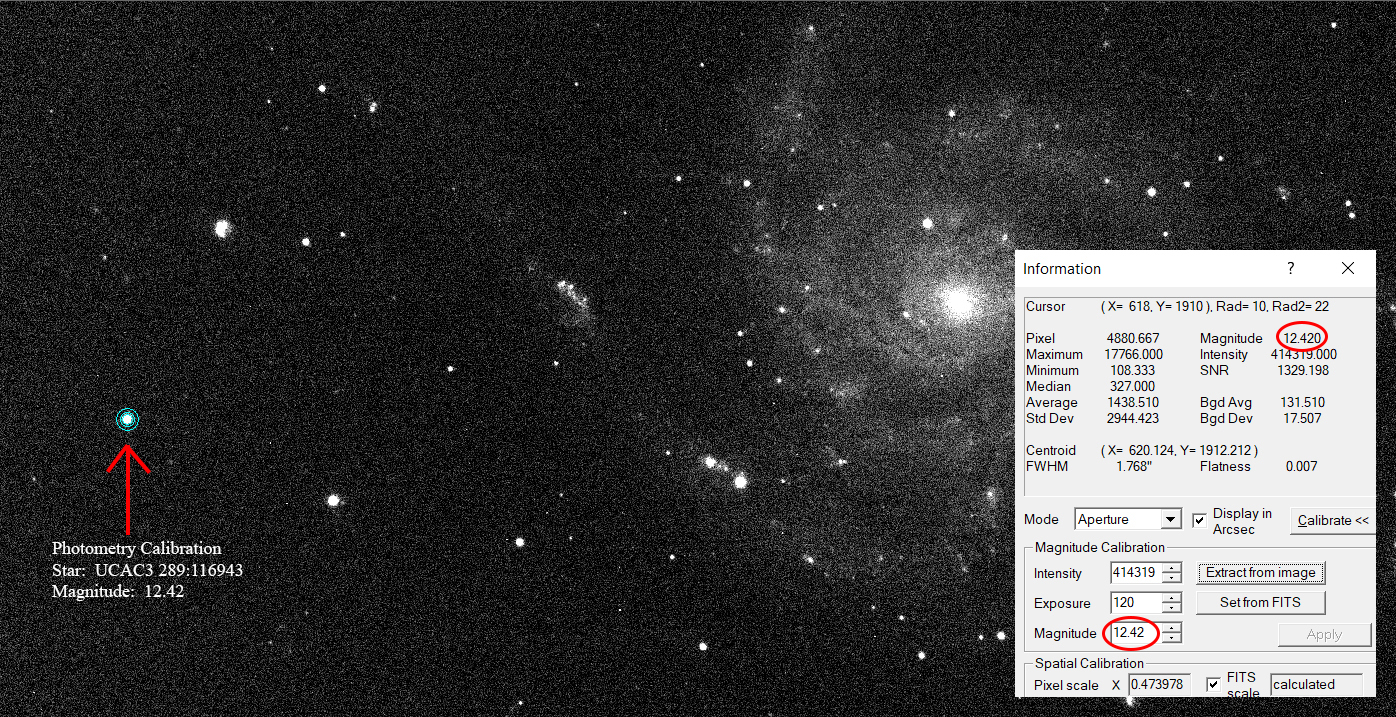
a nearby foreground known UCAC3 Catalog star of known magnitude (see images and
descriptions above).
● The photometry software tools showed the
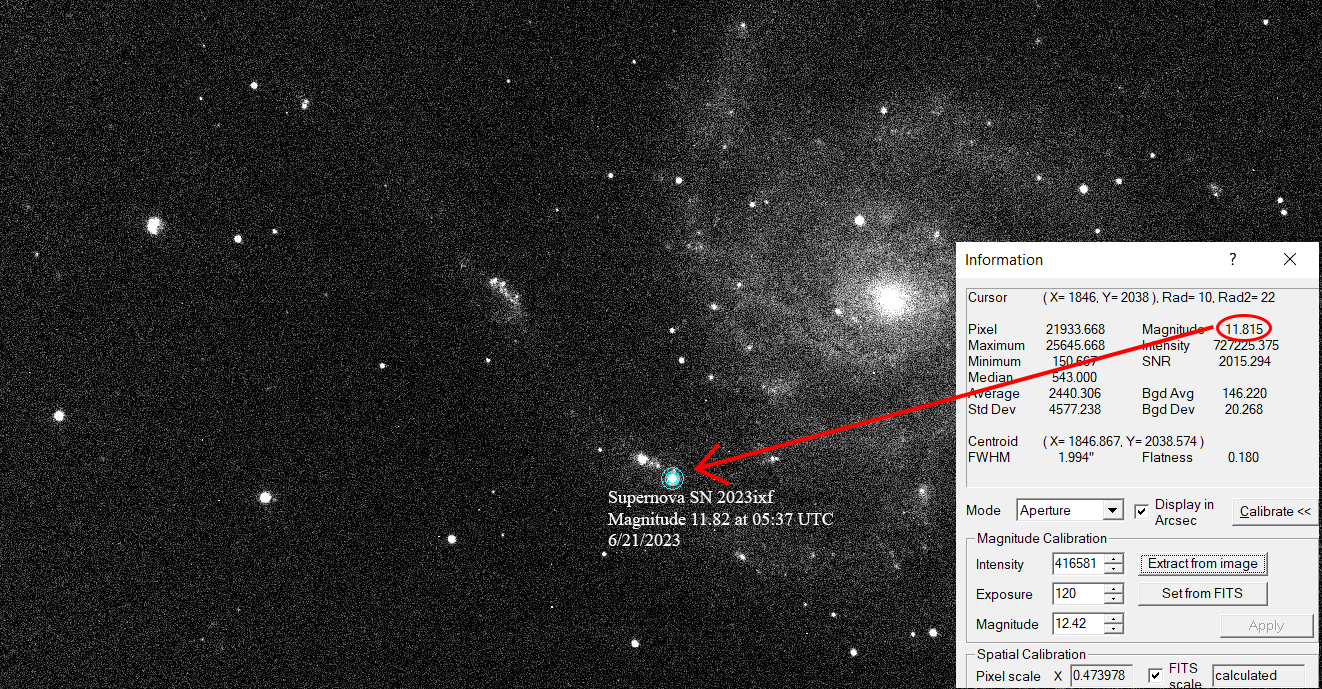
supernova was shining at approximately magnitude 11.82 at 0537 UTC on June
21st, 2023.
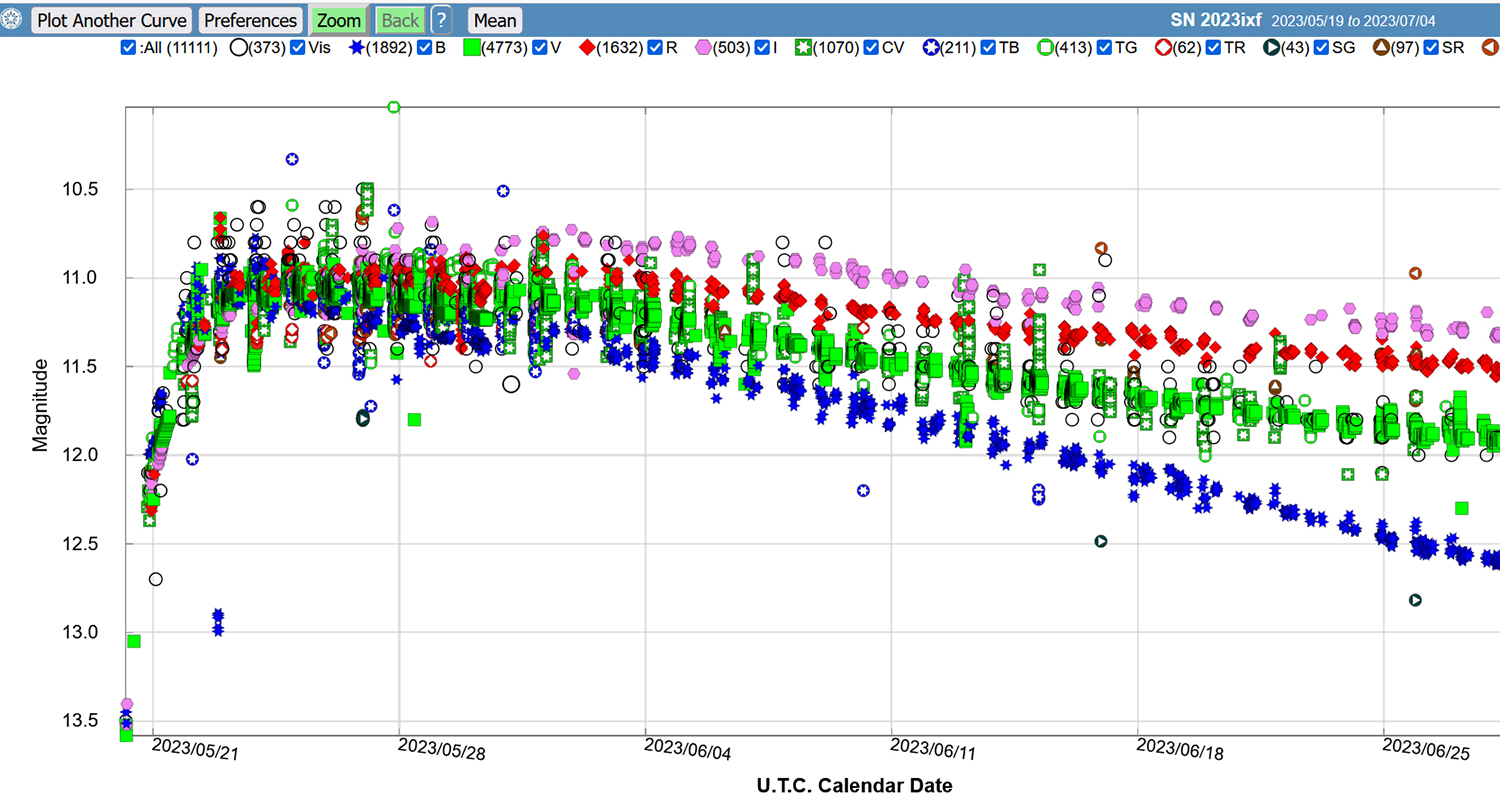
● For comparison, you can view the AAVSO brightness chart
below, showing the supernova brightness data over a period of several days.
Supernova Photometry Information and Locator Image shown below:
First image below explains the Photometry Software Calibration methodology. A nearby star in the same region of the image as the supernova and similar in brightness level was used to calibrate the Maxim Photometry Software Tool. The images shown below are both still in linear, non-stretched form. They were shot in RGB color with an OSC camera, then converted by software to mono format. They have been noise-reduced with matching Dark, Flat and Flat-Dark Calibration frames prior to using the software Photometry measurements:
Next image below shows the location and software-measured brightness of supernova SN 2023ixf in one of the spiral arms of the galaxy at a distance of approximately 23 million light-years from Earth. It was shining at Magnitude 11.82 in the early morning hours of June 21st, 2023:
Next image shown below is a Photometry Chart courtesy of AAVSO that shows the brightness levels of the supernova by calendar date:
 |
|
|
Older M101 Data From 2005 Shown Below:
Image Details:
Page last updated: 7/7/2023 |